CUDA API Remoting技术
CUDA的虚拟化有一项技术为 API Remoting,
通俗点就是将编程API重定向,或者说远程过程调用。这是在接口层面上实现虚拟化, 采用对调用接口二次封
装的方法。 API
重定向虽然能够达到接近原生硬件的性能, 但是需要修改客户虚拟机中程序库。本文探究CUDA
runtime API的重定向细节。
Runtime API
CUDA 应用程序可以调用CUDA Library,CUDA Runtime API和CUDA Driver
API。 其中 CUDA Runtime API 还调用了 Driver API。Runtime API以动态库
libcuda.so 提供,使用 ioctl 通过
/dev/nvidia0,/dev/nvidia-uvm,/dev/nvidiactl
与Driver(kernel mode)交互。 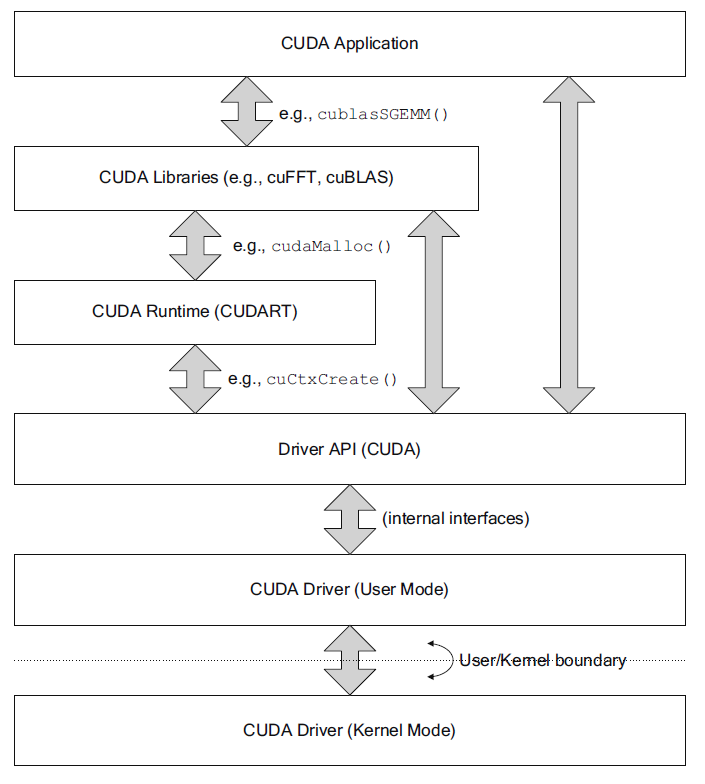
nvcc 对CUDA库的默认的链接方式是静态链接。可以通过
ldd 查询,未发现关于
libcudart.so的动态链接库。 其实可以通过 nvcc
编译过程来发现端倪。
1 | GPU$ nvcc --verbose thread.cu -o staticthread |
#$ nvcc warning : The 'compute_20', 'sm_20', and 'sm_21' architectures are deprecated, and may be removed in a future release (Use -Wno-deprecated-gpu-targets to suppress warning).
- 读取环境变量
#$ SPACE= #$ CUDART=cudart #$ HERE=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin #$ THERE=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin #$ TARGET_SIZE= #$ TARGET_DIR= #$ TARGET_SIZE=64 #$ TOP=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/.. #$ NVVMIR_LIBRARY_DIR=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/../nvvm/libdevice #$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/../lib::/usr/local/cuda-8.0/lib64 #$ PATH=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/../open64/bin:/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/../nvvm/bin:/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin:/home/max/bin:/usr/local/> sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin:/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin #$ INCLUDES="-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include"
#$ LIBRARIES= "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64/stubs" "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64" #$ CUDAFE_FLAGS= #$ PTXAS_FLAGS=
- 使用
C++预处理器进行预处理,生成中间文件.cpp1.ii
讲一些定义好的枚举变量(如cudaError)、struct、静态内联函数、extern c++和extern函数,还重新定义了std命名空间、函数模板等内容,写在main函数之前。
#$ gcc -D__CUDA_ARCH__=200 -E -x c++ -DCUDA_DOUBLE_MATH_FUNCTIONS -D__CUDACC__ -D__NVCC__ "-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include" -D"CUDACC_VER=80061" -D"CUDACC_VER_BUILD=61" -D"CUDACC_VER_MINOR=0" -D"CUDACC_VER_MAJOR=8" -include "cuda_runtime.h" -m64 "thread.cu" > "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-9_thread.cpp1.ii"
- 调用
cudafe将.cpp1.ii分别执行在host和device上代码分离开,生成.cudafe1.gpu和cudafe1.c,其中main函数在.cudafe1.c文件中。
#$ cudafe --allow_managed --m64 --gnu_version=50400 -tused --no_remove_unneeded_entities --gen_c_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-4_thread.cudafe1.c" --stub_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-4_thread.cudafe1.stub.c" --gen_device_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-4_thread.cudafe1.gpu" --nv_arch "compute_20" --gen_module_id_file --module_id_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-3_thread.module_id" --include_file_name "tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-2_thread.fatbin.c" "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-9_thread.cpp1.ii"
- 预处理,由于不同架构gpu的计算能力不同,需要进行相应的处理,生成
.cpp4.ii。
#$ gcc -E -x c++ -D__CUDACC__ -D__NVCC__ "-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include" -D"CUDACC_VER=80061" -D"CUDACC_VER_BUILD=61" -D"CUDACC_VER_MINOR=0" -D"CUDACC_VER_MAJOR=8" -include "cuda_runtime.h" -m64 "thread.cu" > "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-5_thread.cpp4.ii"
#$ cudafe++ --allow_managed --m64 --gnu_version=50400 --parse_templates --gen_c_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-4_thread.cudafe1.cpp" --stub_file_name "tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-4_thread.cudafe1.stub.c" --module_id_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-3_thread.module_id" "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-5_thread.cpp4.ii"
- 使用
c预处理器进行预处理,生成中间文件.cpp2.i
#$ gcc -D__CUDA_ARCH__=200 -E -x c -DCUDA_DOUBLE_MATH_FUNCTIONS -D__CUDACC__ -D__NVCC__ -D__CUDANVVM__ -D__CUDA_FTZ=0 -D__CUDA_PREC_DIV=1 -D__CUDA_PREC_SQRT=1 "-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include" -m64 "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-4_thread.cudafe1.gpu" > "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-11_thread.cpp2.i"
- 调用
cudafe将.cpp2.i分别执行在host和device上代码分离开,生成.cudafe2.gpu和cudafe2.c。
#$ cudafe -w --allow_managed --m64 --gnu_version=50400 --c --gen_c_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-12_thread.cudafe2.c" --stub_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-12_thread.cudafe2.stub.c" --gen_device_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-12_thread.cudafe2.gpu" --nv_arch "compute_20" --module_id_file_name "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-3_thread.module_id" --include_file_name "tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-2_thread.fatbin.c" "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-11_thread.cpp2.i"
- 使用
c预处理器进行预处理,生成中间文件.cpp3.i
#$ gcc -D__CUDA_ARCH__=200 -E -x c -DCUDA_DOUBLE_MATH_FUNCTIONS -D__CUDABE__ -D__CUDANVVM__ -D__USE_FAST_MATH__=0 -D__CUDA_FTZ=0 -D__CUDA_PREC_DIV=1 -D__CUDA_PREC_SQRT=1 "-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include" -m64 "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-12_thread.cudafe2.gpu" > "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-13_thread.cpp3.i"
- 生成
.ptx文件
#$ cicc -arch compute_20 -m64 -ftz=0 -prec_div=1 -prec_sqrt=1 -fmad=1 -nvvmir-library "/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/../nvvm/libdevice/libdevice.compute_20.10.bc" --orig_src_file_name "thread.cu" "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-13_thread.cpp3.i" -o "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-6_thread.ptx"
PTX离线编译,将代码编译成一个确定的计算能力和SM版本,对应的版本信息保存在.cubin中。
#$ ptxas -arch=sm_20 -m64 "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-6_thread.ptx" -o "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-14_thread.sm_20.cubin"
- 生成
.fatbin.c
#$ fatbinary --create="/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-2_thread.fatbin" -64 "--image=profile=sm_20,file=/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-14_thread.sm_20.cubin" "--image=profile=compute_20,file=/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-6_thread.ptx" --embedded-fatbin="/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-2_thread.fatbin.c" --cuda
#$ rm /tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-2_thread.fatbin #$ gcc -D__CUDA_ARCH__=200 -E -x c++ -DCUDA_DOUBLE_MATH_FUNCTIONS -D__USE_FAST_MATH__=0 -D__CUDA_FTZ=0 -D__CUDA_PREC_DIV=1 -D__CUDA_PREC_SQRT=1 "-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include" -m64 "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-4_thread.cudafe1.cpp" > "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-15_thread.ii" #$ gcc -c -x c++ "-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include" -fpreprocessed -m64 -o "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-16_thread.o" "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-15_thread.ii" #$ nvlink --arch=sm_20 --register-link-binaries="/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-7_staticthread_dlink.reg.c" -m64 "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64/stubs" "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64" -cpu-arch=X86_64 "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-16_thread.o" -o "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-17_staticthread_dlink.sm_20.cubin" #$ fatbinary --create="/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-8_staticthread_dlink.fatbin" -64 -link "--image=profile=sm_20,file=/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-17_staticthread_dlink.sm_20.cubin" --embedded-fatbin="/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-8_staticthread_dlink.fatbin.c" #$ rm /tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-8_staticthread_dlink.fatbin #$ gcc -c -x c++ -DFATBINFILE=""/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-8_staticthread_dlink.fatbin.c"" -DREGISTERLINKBINARYFILE=""/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-7_staticthread_dlink.reg.c"" -I. "-I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//include" -D"CUDACC_VER=80061" -D"CUDACC_VER_BUILD=61" -D"CUDACC_VER_MINOR=0" -D"CUDACC_VER_MAJOR=8" -m64 -o "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-18_staticthread_dlink.o" "/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/crt/link.stub"
gcc链接所有目标文件
#$ g++ -m64 -o "staticthread" -Wl,--start-group "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-18_staticthread_dlink.o" "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-16_thread.o" "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64/stubs" "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64" -lcudadevrt -lcudart_static -lrt -lpthread -ldl -Wl,--end-group
注意最后一行 > #$ g++ -m64 -o "staticthread" -Wl,--start-group "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-18_staticthread_dlink.o" > "/tmp/tmpxft_0000286a_00000000-16_thread.o" "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64/stubs" "-L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/..//lib64" > -lcudadevrt -lcudart_static -lrt -lpthread -ldl -Wl,--end-group
这里的链接的库 cudadevrt和 cudart_static
是位于 /usr/local/cuda/lib64 中的
libcudadevrt.a 和 libcudart_static.a 。
通过设置 cuda 的编译选项,使其调用库为动态调用:
--cudart=shared 。 这样编译出来的二进制文件小很多。
1 | -rwxrwxr-x 1 max max 569848 5月 15 09:39 staticthread* |
cuda kernel
github 上的cudahook给出了cuda运行时API的钩子函数,利用了
LD_PRELOAD 和 dlsym 。
之前尝试失败,造成的原因就是 nvcc 静态编译。 修改成动态链接即可。
位于 /usr/local/cuda/include/crt/host_runtime.h中的
1
2
3
4__cudaRegisterFunction
__cudaUnregisterFatBinary
__cudaRegisterFatBinary
__cudaInitModule // 这个目前没用上1
2
3
4
5
6
7cudaMalloc
cudaConfigureCall
cudaLaunch
cudaFree
cudaSetupArgument
cudaMemcpy
qCUDA
今天【2018,6,1】收获颇丰,先是找到一份 API Remoting
的源码qCUDA: GPGPU
Virtualization at a New API Remoting Method with
Para-virtualization。
qCUDA 采用的是虚拟机上的GPU虚拟化,采用
virtio 作为传输通道,但是 kernel
函数没有进行传输,直接将其二进制的客户机物理地址转换(guest physical
address, GPA)到宿主机虚拟地址(host virtual
address,HVA),据说带宽效率达到的95%。
关键部分是在 guest 的驱动中,将用户态
malloc 后的内存,全部通过 copy_from_user_safe
拷贝到在内核中 kmalloc 申请的内存,之后再通过
virt_to_phys 将内核的虚拟地址转换成物理地址。
virt_to_phys: The returned physical address is the physical (CPU) mapping for the memory address given. It is only valid to use this function on addresses directly mapped or allocated via kmalloc. It means It is used by the kernel to translate kernel virtual address (not user virtual address) to physical address
CRCUDA
是的,今天【2018,6,1】收获第二件事就是找到了
pause/resume 的另一份代码:Transparent checkpoint/restart
library for CUDA application.。
【暂时没有研究】
查找二进制中的
fatbin部分
最关键的部分就是如何将包含 kernel 的 GPU
代码从二进制中找到并剥离出来。
还是在what are the parameters for __cudaRegisterFatBinary and __cudaRegisterFunction functions? 此问题下,良心答主给出了建设性意见。
答主提到: __cuRegisterFatBinary 函数的唯一一个
void * 的指针参数,指向的是一个结构体:
1 | struct { |
而这个结构体中的字段 ptr 指向的是真正的
fatBin文件,此fatBin文件按照 fatBinary.h 中的格式定义。
此文件中会有一些其他信息,如果接续搜索下去,会搜索到
0x7F + 'ELF' ,可以再此提取出 cubin 文件。
按照提示,我去做一些尝试!
在 /usr/local/cuda/include/ 中找到
fatBinary.h 文件,并找到了 fat binary 头结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7struct __align__(8) fatBinaryHeader
{
unsigned int magic;
unsigned short version;
unsigned short headerSize;
unsigned long long int fatSize;
};
那么指向此结构体的指针在哪里呢?
这还要从 __cudaRegisterFatBinary
讲起来。它的函数声明为: 1
void** __cudaRegisterFatBinary(void *fatCubin);
这个函数传入的参数 fatCubin
指针是指向的是一个结构体,此结构体定义在
/usr/local/cuda/include/fatBinaryCtl.h 中。 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13/*
* These defines are for the fatbin.c runtime wrapper
*/
#define FATBINC_MAGIC 0x466243B1
#define FATBINC_VERSION 1
#define FATBINC_LINK_VERSION 2
typedef struct {
int magic;
int version;
const unsigned long long* data;
void *filename_or_fatbins; /* version 1: offline filename,
* version 2: array of prelinked fatbins */
} __fatBinC_Wrapper_t;__fatBinC_Wrapper_t 第三个参数就是指向的真是的 fatCubin,而
fatCubin 的最开始的元数据是结构体 struct fatBinaryHeader
。
可以通过 nvcc 编译生成 fatbin 文件,与
截获的文件比较,完全一致。 1
2nvcc --cudart=shared --fatbin -o test.fatbin test.cu
diff test.fatbin cut.fatbin
Trouble
launching CUDA kernels from static initialization code提到了CUDA
runtime程序采取lazy初始化Context,直到调用了第一个CUDA runtime
API,Context才正式初始化。这个初始化的函数入口就是
__cudaRegisterFatBinary ,它负责载入和注册fat
binary中的kernels,textures和静态定义的设备符号。
验证办法就是在用gdb调试时,添加断点
break __cudaRegisterFatBinary 。
CUDA CUBIN/PTX文件动态加载
在获取了GPU的代码后,如何在其他进程中动态加载呢?这就要用到Driver
API的 Module
Management的API了。 其中,涉及到Module的API如下: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18CUresult cuModuleGetFunction ( CUfunction* hfunc, CUmodule hmod, const char* name )
Returns a function handle.
CUresult cuModuleGetGlobal ( CUdeviceptr* dptr, size_t* bytes, CUmodule hmod, const char* name )
Returns a global pointer from a module.
CUresult cuModuleGetSurfRef ( CUsurfref* pSurfRef, CUmodule hmod, const char* name )
Returns a handle to a surface reference.
CUresult cuModuleGetTexRef ( CUtexref* pTexRef, CUmodule hmod, const char* name )
Returns a handle to a texture reference.
CUresult cuModuleLoad ( CUmodule* module, const char* fname )
Loads a compute module.
CUresult cuModuleLoadData ( CUmodule* module, const void* image )
Load a module's data.
CUresult cuModuleLoadDataEx ( CUmodule* module, const void* image, unsigned int numOptions, CUjit_option* options, void** optionValues )
Load a module's data with options.
CUresult cuModuleLoadFatBinary ( CUmodule* module, const void* fatCubin )
Load a module's data.
CUresult cuModuleUnload ( CUmodule hmod )
Unloads a module.
可以使用 cuModuleLoad 将 fatbinary image从文件读入。而
cuModuleLoadData 将 fatbinary image从字符串读入。
cuModuleGetFunction 可以从 module hmod
当中返回函数名为 name 的函数指针 hfunc。
cudaLaunchKernel
通过 nvprof 工具获得简单的 vectorAdd
程序的profile,可以获得一些额外的信息。
==16486== Profiling application: ./vectorAdd
==16486== Profiling result:
Type Time(%) Time Calls Avg Min Max Name
GPU activities: 65.79% 67.266us 2 33.633us 32.737us 34.529us [CUDA memcpy HtoD]
30.52% 31.200us 1 31.200us 31.200us 31.200us [CUDA memcpy DtoH]
3.69% 3.7760us 1 3.7760us 3.7760us 3.7760us vectorAdd(float const *, float const *, float*, int)
API calls: 99.23% 127.05ms 3 42.351ms 3.4780us 127.05ms cudaMalloc
0.34% 430.20us 96 4.4810us 98ns 170.55us cuDeviceGetAttribute
0.21% 263.80us 3 87.934us 49.895us 120.54us cudaMemcpy
0.11% 141.99us 1 141.99us 141.99us 141.99us cuDeviceTotalMem
0.07% 91.916us 3 30.638us 3.8710us 80.965us cudaFree
0.03% 38.155us 1 38.155us 38.155us 38.155us cuDeviceGetName
0.01% 18.698us 1 18.698us 18.698us 18.698us cudaLaunchKernel
0.00% 1.8070us 1 1.8070us 1.8070us 1.8070us cuDeviceGetPCIBusId
0.00% 959ns 3 319ns 82ns 545ns cuDeviceGetCount
0.00% 794ns 2 397ns 139ns 655ns cuDeviceGet
0.00% 193ns 1 193ns 193ns 193ns cuDeviceGetUuid
0.00% 186ns 1 186ns 186ns 186ns cudaGetLastErrorvectorAdd源码只有 cudaMemcpy 、
cudaFree 、
cudaMalloc,这莫名多出了很多函数。说明再载入二进制的时候又默认启动了其他相关的函数。
GPGPU-SIM
经过了上面艰难的探索,今天偶然发现一篇对CUDA程序编译和调用过程的探索,这篇GPGPU-SIM Code Study (version: 3.1.2) 里面讲解了源码编译模拟过程,其中设计到我们这里探究的隐藏API。同时cudaErrorCudartUnloading问题排查及建议方案也做了讨论。
编译器将 __cudaRegisterFatBinary()
总结一下:
nvcc 使用 --cuda 选项来查看
编译的执行配置语法(ECS)和管理kernel代码,生成 .cu.cpp.ii
文件,此文件可以不需要NVIDIA编译工具就能够被编译和链接。深入阅读此文件,就可以发现端倪。
1. 设备代码被作为 fat binary 对象嵌入到可执行文件的 .rodata
区间。 2.
对于kernel代码,源码中都有对应的与每个kernel函数名相同的host函数。 3. 在
main 函数调用前,cudaRegisterAll
函数做以下工作。 - 调用入口函数
__cudaRegisterFatBinary,参数是指向 fat binary
的指针,此指针可以直接访问kernel代码。 -
为每个kernel,调用kernel注册函数cudaRegisterFunction,指针指向在上述步骤2中源码中的函数。
4. 对于执行配置语法被以下函数取代: + cudaConfigureCall
用于设置kernel调用的配置选项,如grid,block等。 +
cudaSetupArgument 用于设置kernel调用的参数。 +
cudaLaunch 调用kernel,参数是指向步骤2中的函数的函数指针。
5. Fat
binary注销函数cudaUnregisterBinaryUtil,在程序退出的时候调用。
函数定义在 /usr/local/cuda/include/crt/host_runtime.h 。
1 | extern void** CUDARTAPI __cudaRegisterFatBinary( |
函数定义在 /usr/local/cuda/include/crt/host_runtime_api.h 。
1
2
3extern __host__ cudaError_t CUDARTAPI cudaConfigureCall(dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, size_t sharedMem __dv(0), cudaStream_t stream __dv(0));
extern __host__ cudaError_t CUDARTAPI cudaSetupArgument(const void *arg, size_t size, size_t offset);
extern __host__ cudaError_t CUDARTAPI cudaLaunch(const void *func);
注意事项
编译问题
- 对
dlopen未定义得引用
在编译时加入动态库 ldl 。 1
gcc -ldl ***
RTLD_NEXTundeclared (first use in this function)
主要是 RTLD_NEXT 没有定义在
posix标准中,因此需要在代码的最开始加上
#define _GNU_SOURCE 。
通过 man dlsym 可以清晰得查看到。
1 | SYNOPSIS |
- error: conflicting types for错误原因
自己在写 cudaMemcpy 函数定义时,是按照CUDA Runtime API
文档写的, 1
2
3
4
5
6
7cudaError_t cudaMemcpy(
void* dst,
const void* src,
size_t count,
cudaMemcpyKind kind)
{
}
可是报错:
1 | error: expected declaration specifiers or '...' before 'cudaMemcpyKind' |
原因包括很多,
-- 没有函数声明,且函数定义在主函数之后;
-- 头文件的被循环引用,在引用时考虑清楚包含顺序
-- 头文件函数声明和函数定义参数不同通过查看 /usr/local/cuda/include/cuda_runtime_api.h:4130
中声明的函数为: 1
2
3
4
5cudaError_t cudaMemcpy(
void* dst,
const void* src,
size_t count,
enum cudaMemcpyKind kind)enum,失声痛哭。
参考:error: conflicting types for 错误原因及解决办法
参考
[1] what are the parameters for __cudaRegisterFatBinary and __cudaRegisterFunction functions? [2] cudahook [3] CUDA CUBIN/PTX文件动态加载 [4] cudaErrorCudartUnloading问题排查及建议方案