NVIDIA GPU虚拟内存(NV50)
本文分析 NVIDIA GPU 的虚拟内存(virtual memory),由
envytools
工具和文档提供。分析的G80显卡(NV50),由于是首代支持虚拟内存的显卡,对于当前使用的显卡已经不适用了,仅供参考。
介绍
G80 一代的显卡的内存管理模块,即MMU,将用户可见的虚拟内存地址转换成设备物理地址。 转换分成两层,DMA对象(如同 x86 的段) 和 页表。 转换包括以下地址空间。
- 逻辑地址:40位的逻辑地址 + channel描述符地址 + DMA对象地址。所有出现在 FIFO 命令描述符中的地址都是逻辑地址,或者最终转换成逻辑地址。
- 虚拟地址:40位的虚拟地址 + channel描述符地址。 指定地址将会在相关channel中的页表中查询。虚拟地址总是逻辑地址转换的结果,并且不能被直接指定。
- 线性地址:40位的线性地址 + 目标区分符(target
specifier)。 区分符可以是 video memory
VRAM、 coherent system memorySYSRAM_SNOOP或者HOST、 non-coherent system memorySYSRAM_NOSNOOP或者NCOH。- VRAM: 32位线性地址,高8位忽略,在设备板上的内存。
- SYSRAM:
40位的线性地址,访问此空间会使得显卡对给定的地址调用PCI/PCIe读写事务,允许访问系统内存(CPU)或者别的PCI设备内存。
SYSRAM_SNOOP使用正常的 PCIe 事务,SYSRAM_NOSNOOP使用PCIe 事务,启用了no snoop位。 大多数时候,线性地址是逻辑地址翻译的结果,但是一些内存区域可以被它们的线性地址直接赋值。
- tag地址:12位的标签地址,用于选择隐藏压缩标签内存的一个小单元,用于VRAM的压缩区域。
- 物理地址:对于VRAM,是内存单元的分表;对于SYSRAM,是最终的总线地址。
虚拟内存(以下简称VM)的作用是将逻辑地址转换成相关的数据,可以转换成设备物理地址或者主机物理地址。
+ linear address addr + target specifier aper:
VRAM , HOST , NCOH 。 + read only
flag ro + supervisor-only flag priv + storage
type: kind
一个特殊值,选择包含数据的内部结构,通过增加cache的局部性来更有效的访问。
+ compression mode: comp + compression tag address:
ctag + partition cycle: + encryption flag:
虚拟内存访问也会以失败结束,比如不在当前页,这就会触发缺页中断。
VM用户
VM被多种用户(client)使用,通常由id区分。 相关的概念是VM引擎(engine),由共享TLBs,并且在一个时刻处于同一channel中的一组用户组成。而对于同一用户,是可能处于不同的VM引擎的。 但是 client + engine 结合并不能区分获取的来源。为了消除歧义, DMA slot ids 也加入了进来。 DMA slot ids也依赖engine和client id。
channel
所有的VM访问都是代表一些channel。一个VM channel 就是一个内存结构体,包括 DMA 对象和页目录(page directory)。 VM channel 也是一个FIFO channel,被PFIFO和FIFO引擎使用并且包含其他数据结构,或者仅仅是一个VM channel,使用非FIFO的引擎。
一个channel由 channel描述符(channel
descriptor)标识,这是一个30位的数,指向了channel内存结构的基址。 +
位0-27:channel内存结构体的12-39位,线性地址。 + 位28-29: channel
内存结构体的target specifier - 0:VRAM; 1:invalid,不使用;
2: SYSRAM_SNOOP or HOST - 3: SYSRAM_NOSNOOP or
NCOH
channel内存结构体包含一些固定偏移的元素,也包含可以放置在结构体内任何位置的channel对象,比如DMA对象。 channel结构体没有固定的大小,尽管channel对象的最大地址是0xffff0。 channel结构体也必须0x1000字节对齐。
原始的G80 channel 有以下固定的元素:
- 0x000-0x200: RAMFC [fifo channels only]
- 0x200-0x400: DMA objects for fifo engines’ contexts [fifo channels only]
- 0x400-0x1400: PFIFO CACHE [fifo channels only]
- 0x1400-0x5400: page directory
而 G84+ 卡使用以下结构体:
- 0x000-0x200: DMA objects for fifo engines’ contexts [fifo channels only]
- 0x200-0x4200: page directory
channel 对象被指定为16字节的偏移从channel结构体的起始位置在 0x10字节单元中。
DMA objects
虚拟内存系统关心的唯一的channel对象是DMA对象。 DMA对象代表了虚拟的或线性的内存中连续的段,是虚拟内存地址转换最开始的步骤。 DMA对象可以分页也可以不分页。 + 未分页的DMA对象直接指定了目标空间和所有属性,仅仅检查基地址和检查限制。 + 分页的DMA对象增加基地址并且在页表中查找它。属性或者来自页表,或者单独被DMA对象覆盖。
DMA对象由16位 selector 区分。在FIFO引擎中,RAMHT
用于将用户可见的32位handles 转换到 selector。 selector
向左位移4位,并且增加到channel结构体基地址来获取DMA对象结构体的地址,
DMA对象结构体的地址是0x18字节长,由32位小端字组成。
- word 0
- bits 0-15: object class. Ignored by VM, but usually validated by fifo engines- should be 0x2 [read-only], 0x3 [write-only], or 0x3d [read-write]
- bits 16-17: target specifier:
- 0: VM - paged object - the logical address is to be added to the base address to obtain a virtual address, then the virtual address should be translated via the page tables
- 1: VRAM - unpaged object - the logical address should be added to the base address to directly obtain the linear address in VRAM
- 2: SYSRAM_SNOOP - like VRAM, but gives SYSRAM address
- 3: SYSRAM_NOSNOOP - like VRAM, but gives SYSRAM address and uses nosnoop transactions
- bits 18-19: read-only flag
- 0: use read-only flag from page tables [paged objects only]
- 1: read-only
- 2: read-write
- bits 20-21: supervisor-only flag
- 0: use supervisor-only flag from page tables [paged objects only]
- 1: user-supervisor
- 2: supervisor-only
- bits 22-28: storage type. If the value is 0x7f, use storage type from page tables, otherwise directly specifies the storage type
- bits 29-30: compression mode
- 0: no compression
- 1: SINGLE compression
- 2: DOUBLE compression
- 3: use compression mode from page tables
- bit 31: if set, is a supervisor DMA object, user DMA object
otherwise
- word 1:
- bits 0-31 of limit address
- word 2:
- bits 0-31 of base address
- word 3:
- bits 0-7: bits 32-39 of base address
- bits 24-31: bits 32-39 of limit address
- word 4:
- bits 0-11: base tag address
- bits 16-27: limit tag address
- word 5:
- bits 0-15: compression base address bits 16-31 [bits 0-15 are forced to 0]
- bits 16-17: partition cycle
- 0: use partition cycle from page tables
- 1: short cycle
- 2: long cycle
- bits 18-19 [G84-]: encryption flag
- 0: not encrypted
- 1: encrypted
- 2: use encryption flag from page tables
首先,DMA对象选择器selector 与0比较。如果selector是0,触发 NULL_DMAOBJ fault。然后,逻辑地址添加到DMA对象基地址中。 作为结果的地址与DMA对象得来的限制地址比较,如果超过了,就触发 DMAOBJ_LIMIT fault。 如果DMA对象分页了,地址就需要到页表中查询,带上 read-only flag, supervisor-only flag, storage type, 和 compression mode。否则该地址直接变成线性地址。 对于压缩的未分页的 VRAM 对象, tag address 由以下组成: + 从中取出计算后的VRAM线性地址,并提取出压缩基地址。如果结果是负值,强制压缩模式为None。 + 将结果向右位移16位。 + 将 base tag 地址加入到结果中。 + 如果 result <= limit tag address,这个tag address可以使用;否则,强制压缩模式为None。
DMA对象限制在的地方通常被称为 "DMA slots", 也就是MMIO registers 或者 FIFO methods。 大部分引擎都缓存着最近使用的DMA对象。 为了 清空这些缓存,通常足够重写 the selector register, 或者重新提交 the selector method。 许多引擎都需要DMA对象的基地址来作好对齐。对齐依赖于引擎和slot。
FIFO引擎内容 dmaobj是值得一提的一组DMA对象。FIFO引擎用其存储每个channel的状态,当给定的channel在相关的引擎中未启用使。 它们的大小和结构体依赖于引擎,它们有固定的 selectors,因此位置在channel结构体中固定的地方。
原始的G80, 对象为:
| Selector | Address | Engine |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0020 | 0x00200 | PGRAPH |
| 0x0022 | 0x00220 | PVP1 |
| 0x0024 | 0x00240 | PME |
| 0x0026 | 0x00260 | PMPEG |
在 G84+ 卡中, 对象变为:
| Selector | Address | Present on | Engine |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0002 | 0x00020 | all | PGRAPH |
| 0x0004 | 0x00040 | VP2 | PVP2 |
| 0x0004 | 0x00040 | VP3- | PPDEC |
| 0x0006 | 0x00060 | VP2 | PMPEG |
| 0x0006 | 0x00060 | VP3- | PPPP |
| 0x0008 | 0x00080 | VP2 | PBSP |
| 0x0008 | 0x00080 | VP3- | PVLD |
| 0x000a | 0x000a0 | VP2 | PCIPHER |
| 0x000a | 0x000a0 | VP3 | PSEC |
| 0x000a | 0x000a0 | MCP89- | PVCOMP |
| 0x000c | 0x000c0 | GT215- | PCOPY |
Page Tables
如果分页的DMA对象被使用了,虚拟地址仍需进一步在页表中查询。 页表分为两层,顶层是0x800条目,页目录。每个条目都包含了0x20000000字节的虚拟内存。
页目录在channel 结构体中,在原始的G80中起始偏移地址为0x1400,在G84+中为0x200。 每个页目录条目或者说 PDE 8字节长。PDE指向了页表,并且指定了页表属性。每个页表可以使用小,中,大页块。 小页块0x1000字节,中页块0x4000字节,大页块0x10000字节。对于小页块,页表的大小可以任意的限制到仅仅覆盖0x2000, 0x4000, 或者 0x8000 页 而不是全部 0x20000 页。超过这个限制的页将会引发缺页。 中页块和大页块页表总是覆盖超过0x8000或者0x2000条目。两种类型的页表都是8字节页表条目或者说PTE。
PDE是由2个32位的小端字组成,有以下的形式:
- word 0:
- bits 0-1: page table presence and page size
- 0: page table not present
- 1: large pages [64kiB]
- 2: medium pages [16kiB] [GT215-]
- 3: small pages [4kiB]
- bits 2-3: target specifier for the page table itself
- 0: VRAM
- 1: invalid, do not use
- 2: SYSRAM_SNOOP
- 3: SYSRAM_NOSNOOP
- bit 4: ??? [XXX: figure this out]
- bits 5-6: page table size [small pages only]
- 0: 0x20000 entries [full]
- 1: 0x8000 entries
- 2: 0x4000 entries
- 3: 0x2000 entries
- bits 12-31: page table linear address bits 12-31
- bits 0-1: page table presence and page size
- word 1:
- bits 32-39: page table linear address bits 32-39
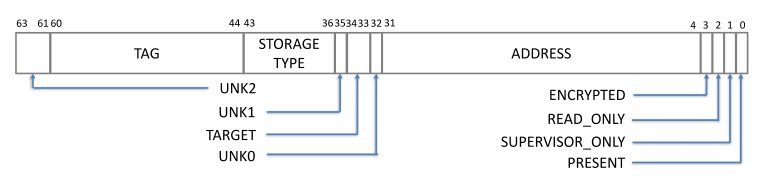
页表起始地址必须 0x1000 对齐。 PTE 由两个32位的小端字word 组成,有以下结构:
word 0:
- bit 0: page present
- bits 1-2: ??? [XXX: figure this out]
- bit 3: read-only flag
- bits 4-5: target specifier
- 0: VRAM
- 1: invalid, do not use
- 2: SYSRAM_SNOOP
- 3: SYSRAM_NOSNOOP
- bit 6: supervisor-only flag
- bits 7-9: log2 of contig block size in pages [see below]
- bits 12-31: bits 12-31 of linear address [small pages]
- bits 14-31: bits 14-31 of linear address [medium pages]
- bits 16-31: bits 16-31 of linear address [large pages]
word 1:
- bits 32-39: bits 32-39 of linear address
- bits 40-46: storage type
- bits 47-48: compression mode
- bits 49-60: compression tag address
- bit 61: partition cycle
- 0: short cycle
- 1: long cycle
- bit 62 [G84-]: encryption flag
TLB flush
页表内容缓存在每个引擎的TLB中。为了清除TLB缓存,TLB flush register 0x100c80 被使用。
MMIO 0x100c80: + bit 0: trigger. When set, triggers the TLB flush. Will auto-reset to 0 when flush is complete. + bits 16-19: 要flush的VM engine
flush操作包括将 engine << 16 | 1
命令写入到此寄存器中,并且等待 位0 变为 0。
源码见 nouveau50.c 的 nv50_vmm_flush()
1 | void nv50_vmm_flush(struct nvkm_vmm *vmm, int level) { |